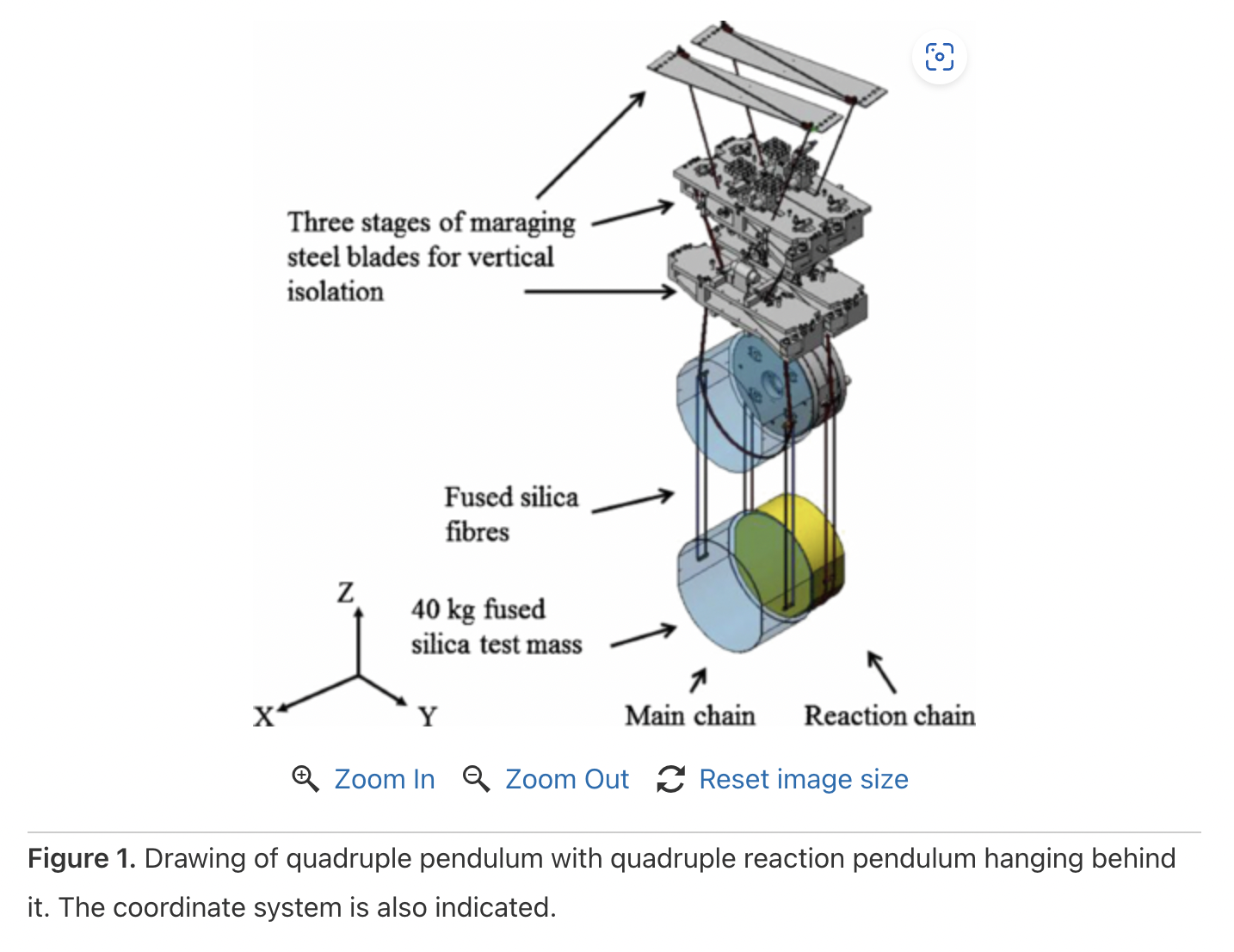
¶ Suspension

LIGO's suspension system plays a critical role in the detection of gravitational waves. The system consists of a quad suspension chain and active isolation systems. The quad suspension chain holds LIGO's test masses (mirrors) perfectly still using a 4-stage pendulum. The mirrors are suspended at the end of four pendulums by 0.4 mm thick fused-silica (glass) fibers. Each node (bolt or washer) in the quad suspension chain is a hefty mass, possessing a lot of inertia. This is in accordance with the Law of Inertia which states that the heavier something is, the more energy it takes to move it. The quad suspensions are themselves mounted below active vibration/seismic isolation systems, which provide the quietest possible environment for operation. Overall, LIGO's suspension system is crucial for maintaining the stability and sensitivity of the interferometer, allowing for the detection of gravitational waves.
¶ Channel Name Breakdown:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Channels | |
| SUS | Suspension |
¶ Suspension Layout: